动手实现一个医学问答大模型(浅尝检索增强生成方法:RAG)
前情提要 & 动机
前段时间忙里偷闲和女朋友一起去了趟云南(你可以查看相册),在出发之前,由于怕女朋友高反,遂问了一圈各种AI应该带什么药、做什么准备措施,以及高反的主要症状等。在做足了功课后,职业病又犯了:我能不能自己搞个大模型小模型,让它具备专业的医学知识,以使得用户提问时,其能从专业的角度给予回答?
说干就干,由于需要一定的实用性,就不考虑 7b 以下的模型了,但7b的模型我的垃圾显卡又训不动,怎么办呢?于是我想起了曾经听说过的一种技术:检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation, RAG),这种方法不需要训练模型,直接用预训练好的模型即可。
RAG是什么?
检索增强生成 (英语:Retrieval-augmented generation, RAG ) 是赋予生成式人工智能模型资讯检索能力的技术。检索增强生成最佳化大型语言模型(LLM) 的交互方式,让模型根据指定的一组文件回应使用者的查询,并使用这些资讯增强模型从自身庞大的静态训练数据中提取的资讯。
维基百科
回到我的需求:使大模型获得一定的医学知识。要使大模型具备一定的专业知识,最方便的不需要额外训练的方法当然就是直接将专业知识作为上下文喂给大模型,让它基于这些内容进行回答。但我们又知道,我们给模型提供的上下文越多,其中的关键信息越会被淡化,哪怕长度未到上限,仍可能引发回答幻觉。
为尽可能减少专业知识领域的幻觉问题,这种名为检索增强生成的方案应运而生。
简单说来,就是通过一些文本相似度算法,从非常多的专业语料数据中检索出与用户的提问相关度较高的内容,一并作为上下文喂给模型。如此,模型的上下文内容中仅仅包含了与用户提问相关度最高的信息,而非所有的专业知识,上下文与用户提问的相关性大幅提升,而其长度则大幅下降,从而使得模型能给出更专业、更可信的回答。
纸上得来终觉浅,在知道其原理后,我们来尝试一下吧!
RAG方法的实践
数据集准备 & 处理
我上哪去弄那么多医学相关的文本数据?逛逛开源社区肯定错不了,稍一搜索,我找到了它:FreedomIntelligence/huatuo_encyclopedia_qa,这是一个中文医学问答数据集,共包含364420条 Q-A 对。
一般情况下,对于大段大段的长篇文本,为了制作RAG的数据库,我们还需要考虑如何将其进行切片,而这种处理好的一条一条的数据就几乎不用考虑切片问题了,特别适合作为RAG的数据。
我们使用一个集成的非常好的框架:langchain来进行处理。RAG方法需要将文本数据制作成嵌入向量存储到数据库中,在检索时匹配语义相似度最高的向量(这里相似度指标可以使用欧氏距离、余弦相似度等)。总之,无论如何,我们总是需要将文本先转化为嵌入向量,因此需要一个嵌入模型,这里我使用了BAAI系列的嵌入模型:BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5。
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5",
model_kwargs={
"device": "cpu"
}
)这里的设备可以改成cuda以提速。有了嵌入模型,接下来我们需要使用一个向量数据库,将全部文本数据转化成的嵌入向量存入。鉴于数据的规模不大,我使用了一个比较轻量的向量数据库:faiss。
langchain对这个数据库进行了比较好的封装,我们可以直接调用:
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from datasets import load_dataset
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
import json
import os
os.makedirs("RAG_DB", exist_ok=True)
data = load_dataset("FreedomIntelligence/huatuo_encyclopedia_qa", split='train')
docs = []
for row in data:
content = json.dumps(row, ensure_ascii=False)
docs.append(Document(page_content=content))
db = None
batchsize = 512
index = 0
with tqdm(range(len(docs))) as bar:
while index < len(docs):
batch = docs[index: index + batchsize]
index += batchsize
if db is None:
db = FAISS.from_documents(batch, embeddings)
else:
db.add_documents(batch)
bar.update(len(batch))
db.save_local("RAG_DB/medical")这一步骤比较耗时,防止等的不耐烦,遂加了个进度条。每次往数据库中添加512条Q-A对,大约花了一个半小时才搞定。
至此,数据已经处理完成。
实现文本检索
既然已经制作好了数据库,这一步就很容易了,langchain同样封装好了相似度计算的部分,它默认使用的是欧氏距离作为相似度指标(距离越小,相似度越高)。我们从数据库对象中提取一个retriever出来,就可以直接使用了:
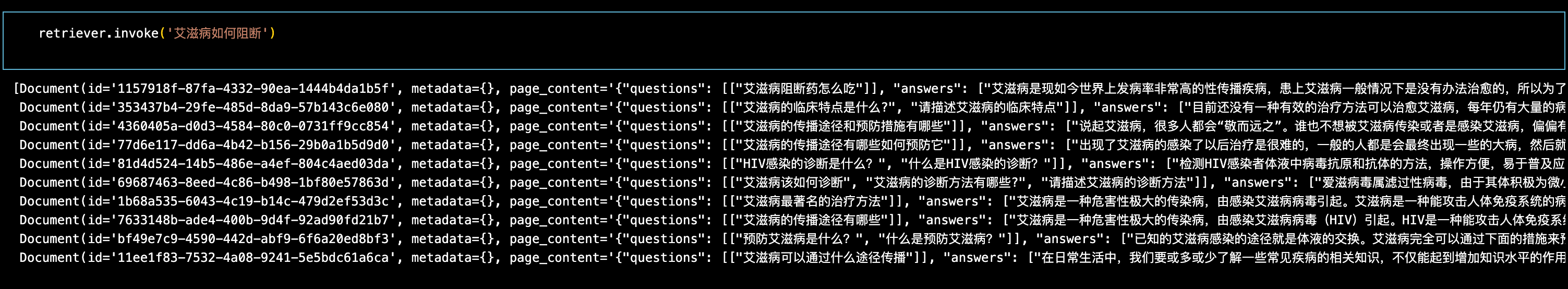
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 10})随便写个问题测试一下:
可以看到检索的效果还是比较好的,拿到了检索器,剩下的操作就很简单了,只要部署起一个大模型,稍微实现一下后端逻辑,再用Gradio整个界面出来,就万事大吉了!
部署大模型
说是大模型,其实就是个7b的小模型罢了。这里我使用了Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct。
将模型下载到本地:
hf download Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct --local-dir ./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct通过vllm启动:
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model ./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct \
--tokenizer ./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct \
--dtype float16 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000 \
--max-num-seqs 4稍等片刻启动完成后(吃掉了约20G显存…(模型自身占用$7\times2=14$GB,KV-cache占用约6.7GB)),我们就可以直接通过OpenAI提供的api来与之交互:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="n"
)
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "你是谁?"}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
messages=messages
)编写RAG业务逻辑
为得到相似度得分,排除掉特别不相关的内容,我们可以自己写一个retrieve函数:
def retrieve(question: str):
docs = db.similarity_search_with_score(question, k=10)
docs = [json.loads(doc.page_content) for doc, score in docs if score.item() < 0.9]
docs = [json.dumps({
"question": doc.get("questions")[0][0],
"answer": doc.get("answers")[0]
}, ensure_ascii=False) for doc in docs]
return docs给一个系统提示词:
system_prompt = """你是一位医学专家。你擅长根据文档回答用户的提问。
要求:
1. 只使用提供的文档内容来回答问题。
2. 不要添加任何额外的内容,如果文档中没有相关信息,请直接回答"无法回答"。
3. 如果没有搜到相关文档,请回答"未查询到相关文档"。
"""再编写一个用户提示词模板:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
文档: {context}
问题: {question}
""")接下来,我们通过langchain框架将RAG的流程实现一下:
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableMap, RunnableLambda
rag_chain = (
RunnableMap({
"history": lambda x: x["history"],
"question": lambda x: build_context_query(x["question"], x["history"])
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"question": x["question"],
"history": x["history"],
"context": retrieve(x["question"]),
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"question": x["question"],
"history": x["history"],
"context": "\n".join(x['context']),
"references": x['context']
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"prompt": prompt_template.format(question=x["question"], context=x["context"]),
"history": x["history"],
"references": x["references"]
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"response": stream(x["prompt"], x["history"]),
"references": x["references"]
})
)这是一个串联过程,看似复杂,实则容易理解,限于篇幅,不再详细解释。
需要解释一下这里定义的一个函数:build_context_query,它用来处理用户输入的提问,如下:
def build_context_query(question: str, history: list) -> str:
"""构建包含历史上下文的查询"""
if not history:
return question
return summarize_context_query(question, history)
def summarize_context_query(question: str, history: list) -> str:
"""使用大模型总结历史提问,生成更准确的检索查询"""
if not history:
return question
# 构建历史对话列表
history = [f'Q: {user_msg}\nA: {response}' for user_msg, response in history[-3:]] # 最近3轮
system_prompt = f"""
你是一个重写助手,任务是将用户当前的问题结合历史对话重写为一个**自包含、清晰明确的问题句子**,以便发送给问答系统。
请遵循以下规则:
1. 仅重写问题,**不回答**;
2. 替换句中的所有代词(如“它”、“这”、“那”等)为具体的名词或短语,当可能存在多个指代对象时,使用最新的历史对话中的信息;
3. 推理指代、补全省略,使问题独立完整;
4. 不引入历史中未提及的信息;
5. 只输出**重写后的问题句子**,不添加任何解释或注释。
"""
summary_prompt = f"""
历史对话:
{chr(20).join([f"{i+1}. {q}" for i, q in enumerate(history)])}
当前问题:
{question}
你重写的问题:
"""
try:
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": summary_prompt}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
messages=messages,
stream=False,
max_tokens=50
)
summarized_query = response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
print(f"原始问题: {question}")
print(f"重写问题: {summarized_query}")
return summarized_query
except Exception as e:
return question这一长串代码,实际仅处理了一件事:根据最近3轮的历史聊天信息,把用户的提问重新整理一下。
在实际使用中,我们发现,用户和模型的对话很可能是这样的:
user: 艾滋病是什么?
assistant: 艾滋病是一种危害性极大的传染病...
user: 它如何治疗?由于RAG在检索召回相似文档时仅仅依赖于用户的提问,而不会关注上下文信息,这里RAG检索的问题:「它如何治疗?」中缺乏关键信息——这个它指什么?(即使用户认为上下文中存在这一信息),为了解决这一问题,我想了个骚操作:让大模型根据历史对话记录来对用户的提问进行重写。这就是上面代码所做的事。
亲测还是比较好用的:
后来发现工程上似乎就是这么做的,这个任务叫Query Rewriting(查询重写)。
需要注意的是,我仅仅在查询重写这一步骤中使用了历史信息,并没有在与大模型的对话上下文中使用它们。
完整代码 & 使用体验
将业务逻辑用Gradio糊一个前端,再实现一下流式响应,一个简单的医学问答大模型平台就完成了!
完整代码如下:
RAG/medical.py
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5",
model_kwargs={
"device": "cpu"
}
)
db_path = 'RAG_DB/medical'
if os.path.exists(db_path):
db = FAISS.load_local(db_path, embeddings, allow_dangerous_deserialization=True)
else:
print("数据库不存在,正在加载数据集...")
from datasets import load_dataset
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
data = load_dataset("FreedomIntelligence/huatuo_encyclopedia_qa", split='train')
docs = []
for row in data:
content = json.dumps(row, ensure_ascii=False)
docs.append(Document(page_content=content))
db = None
batchsize = 512
index = 0
with tqdm(range(len(docs))) as bar:
while index < len(docs):
batch = docs[index: index + batchsize]
index += batchsize
if db is None:
db = FAISS.from_documents(batch, embeddings)
else:
db.add_documents(batch)
bar.update(len(batch))
db.save_local(db_path)
system_prompt = """你是一位医学专家。你擅长根据文档回答用户的提问。
要求:
1. 只使用提供的文档内容来回答问题。
2. 不要添加任何额外的内容,如果文档中没有相关信息,请直接回答"无法回答"。
3. 如果没有搜到相关文档,请回答"未查询到相关文档"。
"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
文档: {context}
问题: {question}
""")
def retrieve(question: str):
docs = db.similarity_search_with_score(question, k=10)
docs = [json.loads(doc.page_content) for doc, score in docs if score.item() < 0.9]
docs = [json.dumps({
"question": doc.get("questions")[0][0],
"answer": doc.get("answers")[0]
}, ensure_ascii=False) for doc in docs]
return docs
def format_references(docs, title="参考内容"):
"""将 Document 列表格式化为折叠式 Q-A Markdown 文本"""
qa_blocks = []
for i, doc in enumerate(docs, 1):
content = json.loads(doc)
question = content.get("question")
answer = content.get("answer")
qa_blocks.append(f"Q{i}: {question}\n\n<details><summary>A{i}:</summary>\n\n{answer}\n\n</details>")
body = "\n\n---\n\n".join(qa_blocks)
markdown = f"<details><summary>{title}</summary>\n\n{body}\n\n</details>"
return markdown
TITLE = '医学RAG问答系统'
DESCRIPTION = '输入医学问题,我会基于专业内容为你解答。'main.py
import gradio as gr
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableMap, RunnableLambda
from openai import OpenAI
from RAG.medical import *
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=FutureWarning)
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="n"
)
def stream(prompt: str, history=None):
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": system_prompt})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
messages=messages,
stream=True
)
for chunk in response:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
yield chunk.choices[0].delta.content
def summarize_context_query(question: str, history: list) -> str:
"""使用大模型总结历史提问,生成更准确的检索查询"""
if not history:
return question
# 构建历史对话列表
history = [f'Q: {user_msg}\nA: {response}' for user_msg, response in history[-3:]] # 最近3轮
system_prompt = f"""
你是一个重写助手,任务是将用户当前的问题结合历史对话重写为一个**自包含、清晰明确的问题句子**,以便发送给问答系统。
请遵循以下规则:
1. 仅重写问题,**不回答**;
2. 替换句中的所有代词(如“它”、“这”、“那”等)为具体的名词或短语,当可能存在多个指代对象时,使用最新的历史对话中的信息;
3. 推理指代、补全省略,使问题独立完整;
4. 不引入历史中未提及的信息;
5. 只输出**重写后的问题句子**,不添加任何解释或注释。
"""
summary_prompt = f"""
历史对话:
{chr(20).join([f"{i+1}. {q}" for i, q in enumerate(history)])}
当前问题:
{question}
你重写的问题:
"""
try:
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": summary_prompt}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="./model/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
messages=messages,
stream=False,
max_tokens=50
)
summarized_query = response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
print(f"原始问题: {question}")
print(f"重写问题: {summarized_query}")
return summarized_query
except Exception as e:
return question
def build_context_query(question: str, history: list) -> str:
"""构建包含历史上下文的查询"""
if not history:
return question
return summarize_context_query(question, history)
rag_chain = (
RunnableMap({
"history": lambda x: x["history"],
"question": lambda x: build_context_query(x["question"], x["history"])
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"question": x["question"],
"history": x["history"],
"context": retrieve(x["question"]),
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"question": x["question"],
"history": x["history"],
"context": "\n".join(x['context']),
"references": x['context']
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"prompt": prompt_template.format(question=x["question"], context=x["context"]),
"history": x["history"],
"references": x["references"]
})
| RunnableLambda(lambda x: {
"response": stream(x["prompt"], x["history"]),
"references": x["references"]
})
)
def qa_interface(message, history):
result = rag_chain.invoke({"question": message, "history": history})
generator = result["response"]
references = result["references"]
response = ""
for token in generator:
response += token
yield response
references_text = format_references(references)
response += "\n\n" + references_text
yield response
chat = gr.ChatInterface(
fn=qa_interface,
title=TITLE,
description=DESCRIPTION
)
chat.launch(server_name="0.0.0.0")使用体验如下: